COPD stands as one of the principal medical issues affecting the United States population. Millions of people suffer from this condition, which results in an excessive workload for healthcare providers. Medical professionals must provide the correct diagnosis coding when treating COPD patients.
The unspecified form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease appears in ICD-10 code J44.9. Healthcare providers oversee patients’ complicated healthcare needs, particularly during polypharmacy ICD-10 situations.
The upcoming discussion reveals the fundamental aspects of ICD-10 code J44.9, including its definition and associated symptoms, together with necessary documentation techniques and essential billing information.
An Overview of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is a widespread respiratory disease that affects millions of people around the world. This disease is a progressive disorder of airways and lung function that leaves individuals constantly battling for breath.
Characterized by symptoms such as chronic coughing, increased mucus production, and persistent breathlessness, COPD requires a comprehensive approach to management.
Common Symptoms of COPD
COPD produces different symptom patterns in individual patients who have this disease. Some common signs include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during activity
- Chronic cough
- Wheezing
- Tightness in the chest
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Fatigue
The symptoms of COPD become increasingly severe as the condition advances, which forces patients to battle with basic everyday tasks. Over time, patients with COPD might need oxygen treatment as a medical intervention.
How Is COPD Classified?
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) primarily has two types, each signifying different pathological procedures:
Classification
Chronic Bronchitis: With persistent inflammation of the bronchial tubes comes increased mucus and a chronic cough. The end result is usually some form of infection in your respiratory system or maybe even just coughing up part of that lung lining.
Emphysema: With the gradual breakdown of air sacs in your lungs, reduced lung elasticity happens. This makes it difficult to breathe, like trying to blow up a balloon that has already been inflated.
Understanding these two classifications is fundamental for healthcare professionals in accurately diagnosing and managing COPD and for researchers to further advance their understanding of the disease. Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are distinct yet interconnected parts of this complex condition, so patient care policies must be tailored individually.
The Appropriate Icd-10 Code for COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is frequently coded as J44.9 in ICD-10 when it is not clearly indicated as acute vs. chronic, with or without exacerbation. Accurate use of coding is important to maintain accurate medical records and to allow healthcare providers to identify symptoms and outcomes of treatment.
Below are the pertinent ICD-10 codes:
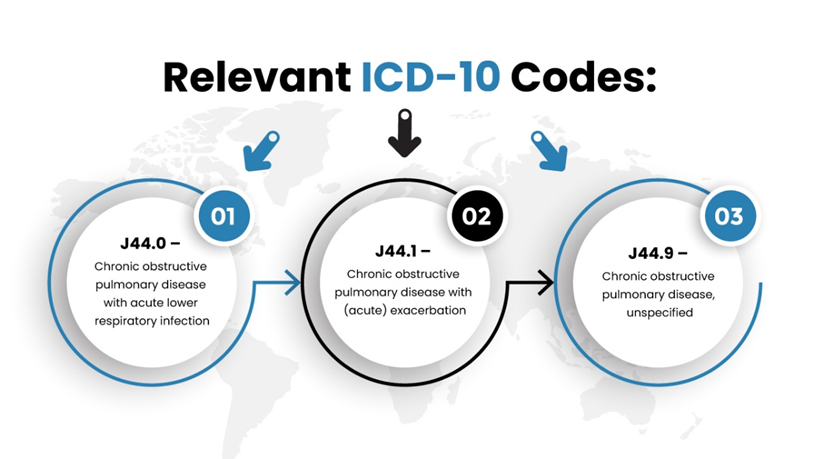
J44.0 —Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) with acute lower respiratory infection
J44.1 —Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease with acute exacerbation
J44.9—Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, unspecified
Each of these codes helps doctors and medical staff share clear and specific information. The outcome supports better care and a fuller understanding of a patient’s respiratory health.
How COPD Develops
Cigarette smoking functions as the primary factor that leads to COPD development within the U.S. population. In addition to cigarette smoking the persistent exposure to air pollutants together with dust and chemicals leads to COPD development. A limited number of COPD cases develop because of the genetic Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency condition.
The majority of patients fail to detect their COPD until their lungs experience extensive damage. The importance of early at-risk patient screening is substantial because it helps detect the disease before serious lung damage occurs.
Diagnosing COPD
Diagnosing COPD involves several steps.
- A medical professional reviews past healthcare information of a patient along with their symptoms before testing the patient.
- The diagnosis of COPD depends heavily on using pulmonary function test results especially through spirometry testing. The test reveals how patients breathe using their lungs whereas it tracks lung volumes and flow rates.
- Chest X-rays together with CT scans serve to eliminate other lung conditions such as cancer or heart failure from consideration.
- The physician may prefer blood testing to measure oxygen levels in the patient.
- When documentation lacks specificity healthcare providers use J44.9 as their coding option.
Medical documentation requiring full clinical details plays an essential role to achieve correct coding and healthcare delivery.
ICD-10 Coding Guidelines for COPD Management
The optimal role of COPD depends on the quality of the underlying ICD-10 codes used to support management programs. Providers can use coding protocols to document the details of their patients’ COPD conditions, including both the type of COPD a patient is experiencing as well as the severity, and collecting this information allows for more targeted and focused patient care.
Targeted Condition Stratification: Distinguish between acute and chronic COPD for an integrated patient assessment and strategic care plan.
Clinical Identification of Exacerbations: Codes can be used for continual patient monitoring, which means the healthcare provider can monitor the efficiency of treatment and make changes when necessary.
Continuous Evaluation and Adjustment: Utilize codes for ongoing patient monitoring, enabling healthcare providers to assess treatment efficacy and make necessary adjustments.
Integrated Practice Standards: The use of ICD-10 codes creates a uniform, standardized model for managing COPD in multiple healthcare settings
These guidelines not only help with proper documentation but also aid in communication and ultimately improve the quality of care for patients with COPD. Especially for practices that also use wc collections services in ca, treating COPD cases due to occupational hazards means proper coding is even more important.
Managing Changes in COPD Diagnostic Coding
Given that this gives way to a more dynamic management of COPD, healthcare professionals need to keep abreast of the changes in the ICD-10 codes. Adjusting to new COPD codes ensures accurate documentation and quality patient manuals. Understanding and coping with changes requires being mindful and on top of respiratory updates.
Providers are key to adapting to the changing ICD-10 COPD codes, with the understanding that the changes reflect current advances in healthcare. Accurate coding, along with thorough assessment and care plans for patients, will only happen provided you are aware.
A commitment to advancing the quality and accuracy of care in an evolving healthcare environment, but adopting changes to the COPD codes.
Billing Challenges with COPD Patients
Treatment of COPD can be a tricky thing to bill for. Bad code results in denials, slowdowns, and compliance problems. It is critical to train clinical staff on best practices for documentation. Coders need to keep up with CMS’s guidance and payer policies as well.
Another problem is managing care transitions. It’s also crucial to learn which treatments work best and when. Because many COPD patients shuttle between primary care offices, specialists, hospitals and rehab centers. Consistent communication with doctors and providers is essential for accurate billing and excellent care.
Utilizing a knowledgeable urgent care billing company will streamline your process. These firms can help with code audits, compliance checks and claim follow-ups. They may also offer training for clinic staff to enhance documentation and minimize errors.
Conclusion
With the constant development in the field of COPD, the incorporation of ICD-10 code J44.9 serves as an essential cornerstone of accuracy and collaborative care. The commitment to adapt to the shifts in the changes made in the medical field is nothing less than a novel approach towards ensuring maximum possible patient care.
By adopting this proactive approach, healthcare professionals can maintain a level of readiness and knowledge that puts them at the cutting edge of COPD management.
This proactive approach not only simplifies documentation workflows, but also plays an important role in improving the quality of care in the COPD population. It highlights that continuous education in medicine will always remain relevant because an updated knowledge base is a prerequisite for holistic and customized care of patients with COPD.