Entity codes for medical billing are identifiers that are assigned for different people involved in a healthcare transaction. These codes specify the roles of all participants in the payment chain, including providers, payers, and patients.
When filing claims, entity codes function to associate these parties with what they are responsible for. For instance, they help specify whether a person is the billing provider, a facility, a customer, or a different service provider.
For example, you submit a claim for a patient who received physical therapy. Could the claim end up in some limbo of confusion, without unique entity codes to distinguish the therapist from the billing office or the billing office from the insurance payer? Entity codes simplify things and also make sure there is no ambiguity.
Entity codes are a component of the broader context of the invoicing codes that are employed to process claims. Procedural codes, such as PRP injection CPT codes, interact with entity codes to ensure effective claim processing. Without them, even properly coded medical procedures can be delayed or denied.
Let’s Have Some More Detail…
Entity codes are used to designate the participants in a transaction, including the healthcare provider, facility, payer, and patient. These codes serve as unique identifiers for payers to process claims appropriately and associate all participants involved with a service.
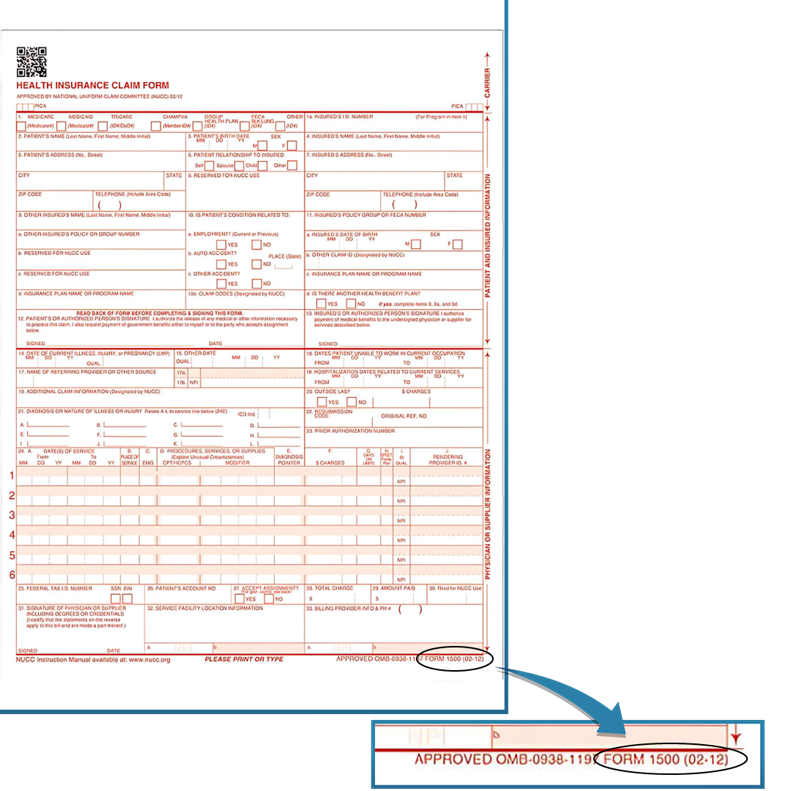
The entity code is entered in a specific section on the standard 1500 form. Look at Box 33b, where you will find key information, including the billing provider NPI or TIN. Claims processing is simplified by the precise incorporation of entity codes.
For instance, if you’re billing for a knee injection procedure, the entity code associates the patient with the service, the facility at which the procedure took place, and the insurance company that will cover the bill. This denotes the precise placement of providers, patients, and payers within the transaction chain.
How Entity Codes Fit into the Medical Billing Process
When healthcare providers bill insurance companies, entity codes are crucial in identifying which organization or professional has provided the service. These codes may help the insurance company apply the payment correctly. Claims may be denied or delayed without one legitimate entity code.
For instance, if you run a practice with services such as PRP injections for joint pain, you must add the correct CPT code. The CPT code for PRP injections defines the treatment. However, the insurance company may deny the claim if it gets confused by the entity code that identifies which provider is providing the service. Correct coding, including entity codes, is the responsibility of the healthcare provider or their medical billing service, and it must match the services provided.
Moreover, entity codes allow insurance companies to accurately authenticate claims and payment history for every provider. This system avoids fraud, eliminates mistakes, and accelerates the whole process. Therefore, familiarizing oneself with entity codes is essential to keeping accurate billing records and making sure payments are received on time.
What is an Entity Identification Number?
The Entity Identification Number, a unique identifier, is issued by healthcare organizations for the purpose of documentation and payment processing. The alphanumeric combination acts as a digital fingerprint, enabling smooth interaction between medical practitioners and insurers.
The medical billing process allocates an Entity Identification Number to each member to ensure uniqueness. This method simplifies what is often a complicated billing system, ensuring that payments are processed correctly.
The Different Types of Entity Identifiers
Different Factors When Defining Entity Identifiers. The following are some common examples illustrating their purpose and function:
National Provider Identifier (NPI): A numerical code used in the United States to identify physicians in billing and administrative activities.
Tax Identification Number (TIN): Issued by the IRS, this number is used for tax purposes by healthcare entities other than providers and may appear on medical billing records.
Employer Identification Number (EIN): Identifies entities that facilitate transactions, taxes, and billing tasks for businesses, including healthcare providers.
Unique Physician Identification Number (UPIN): Before the introduction of the NPI, the unique physician identification number (UPIN) was the national identifier; in some scenarios, the UPIN is still used.
Medicare Provider Number: This is a specific number used to identify practitioners and organizations that are enrolled in Medicare. This information is very important for processing payments and claims connected with Medicare.
Entity Code Denial
Whether you are preparing to submit either an initial claim or an appeal, knowing an entity code denial cannot be overstated. What is entity code denial? An entity code denial is a claim denial related to the entity code on the billing documentation. It may be due to errors, contradictions, or nonconformity with the current coding guidelines.
In simple terms, it indicates that the identifier, which is added in the claim provided by a healthcare provider, did not fulfill the requirements laid down by the payer or government organizations. As healthcare providers move toward the goal of appropriate reimbursement, identifying the reasons for denials of provider entity codes can play a key role in recognizing and rectifying issues quickly, resulting in a more streamlined revenue cycle.
Common Causes of Entity Code Denial
Rejections from the Entity Code can result from reasons such as errors, omissions, and violations of coding standards. Understanding the explanations for these denials is essential to resolving problems in a timely manner, which will help avoid reimbursement delays.
1. Incorrect Entity Code Information
Mistakes in the entity code submitted, be it due to typos, outdated code, or any such error, may also result in rejection. This granularity is critical for successful claims processing, as it requires precise input of this information.
2. Omission of the Entity Code
The absence of a required entity code from the claim documentation may lead to instant rejection. This error often occurs due to the incomplete or improper review of claim forms before submission.
3. Non-Adherence to Coding Standards
Payers and governing bodies establish coding standards that require entity codes. Applying less than what these predefined rules require in the submittal code could lead to a claim rejection.
4. Expired Codes
The use of an expired code will flag the claim because certain entity codes have validity periods. Keeping up with active and valid codes is a major factor in avoiding this type of denial.
5. Mismatched Entity Details
Claims are likewise denied when the entity code differs from other accompanying entity-related records. If the name or address associated with the Entity Code doesn’t match the claim, the submission may be rejected.
Entity Codes in Action: Examples for Common Medical Specialties
PRP Billing
Among the medical treatments for various injuries and chronic conditions, PRP (platelet-rich plasma) injections have gained popularity. PRP injections provide a wide range of benefits, from healing sports injuries to rejuvenating dermatologic skin conditions. However, precision is critical when billing for such innovative treatments.
For example, a practice may charge for performing PRP injections with a CPT code for PRP injections. Entity codes differentiate between various types of entities (e.g., the physician administering the injection) and exclude the facilities supplying the equipment. This piece of information enables insurance processes to rapidly identify and verify each component of the claim, facilitating the prevention of delays.
Urology Billing
Like obstetrics and gynecology, urology may have its own series of tests and procedures. For example, a single patient may visit many providers, such as surgeons, laboratories, and imaging centers. You must accurately identify each of them by using their entity codes.
Say, for instance, a claim tied to an imaging service for kidney stones: entity codes clarify that the lab’s involvement is distinct from the role of the urologist. A well-trained urology billing company makes sure to use these identifiers to reduce errors while speeding up payments.
Action Steps for Healthcare Providers
Entity codes are a vital part of the medical billing process. They make it easier to identify providers and facilities, enhance payment accuracy, and reduce errors. With best practices, technology investments, and expert help when needed, healthcare providers can keep their revenue cycle running smoothly.
It would be valuable to review your current billing practices. Small tweaks can have an immense impact, such as controlling your entity code for PRP CPT code billing, conducting a professional urology billing partnership, or considering medical billing services California.
Start billing easier now!